Sustainable Tourism, Green Tourism, Ecotourism Explained

Sustainable tourism is now a new way of practicing tourism.
As it is, tourism plays an important role in the economy of most countries. In the past, mass tourism led to several detrimental impacts on the environment, physically and socio-culturally. But, since the environmental movement in the 1970s/80s, the focus of the tourism sector changed. The well-being of the host community became the priority instead of the tourists.
Over time, people used several terms to define this new type of tourism. Some examples are alternative, endemic, sustainable, eco and green tourism.
And eventually, different organizations defined the different terms in relation to the purpose of the tourism activity.
We will concentrate on the definitions of sustainable tourism, ecotourism and green tourism mainly. Though people use these three terms interchangeably, they actually refer to different things.
Sustainable tourism
History of sustainable tourism
Since the 1992 Earth Summit in Rio, all economic sectors had to decrease their environmental impacts. They were compelled to be more sustainable. Sustainable here refers to economic vitality, social equity and environmental preservation. The tourism sector, one of the largest global industries, had to comply as well.
In the early days, tourism suppliers basically supported environmental conservation. Many also advocated for the preservation of local culture and traditions. But, generally, researchers, businesses and academicians mostly debated the idea of sustainable tourism. The media also did not give it much attention.
As the years rolled by and the threats of climate change became more visible, sustainable tourism became an obligation.
Definition of sustainable tourism
According to the UNWTO,
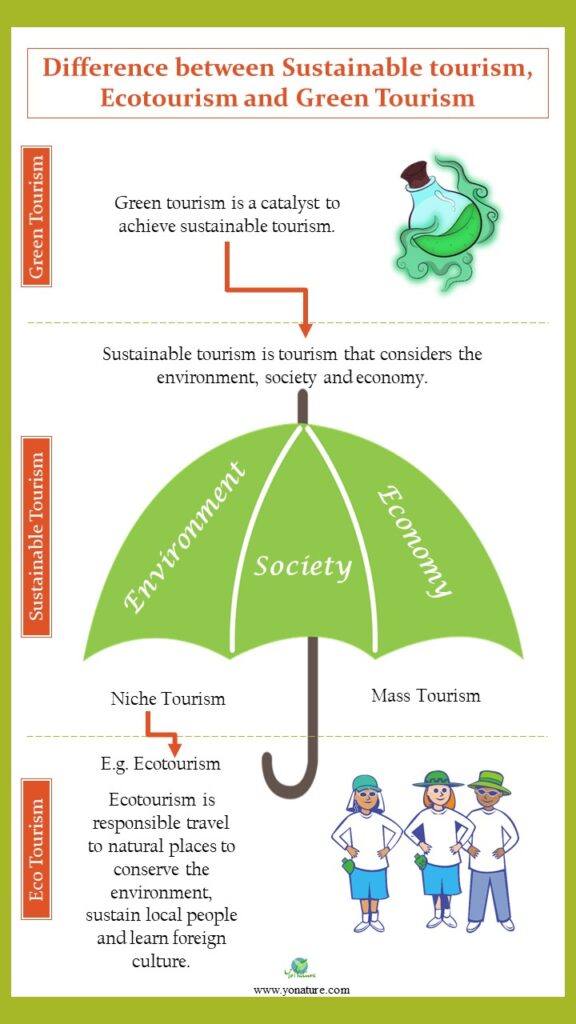
Sustainable tourism is tourism that takes full account of its current and future environmental, social and economic impacts. It addresses the needs of visitors, the environment, host communities and the industry.
Basically, sustainable tourism is the integration of the sustainable development principles into the tourism sector. A harmony must exist between the environment, economy and society.
Hence, it is not a sub-sector of tourism per se. Rather, it is an umbrella under which all forms of tourism fall, including eco-tourism.
Sustainable tourism rests on specific development guidelines and management practices. It also includes both mass and niche tourism.
Principles of sustainable tourism
Basically, the principles for sustainable tourism are
- Using environmental resources wisely,
- Respecting and conserving socio-cultural authenticity of host communities
- And providing economic benefits to host communities.
Thus, sustainable tourism is quite complex in nature and requires the efforts of all stakeholders including the government. It is also a continuous process, with adjustments as required.
At the same time, the experience must enrich the tourist significantly. It must raise awareness of environmental issues. And encourage sustainable gestures.
Ways to be sustainable in the tourism sector
So, all stakeholders play an important role in making the tourism sector sustainable. It includes small, local operations to large, international companies. As it is, the sector provides various services like accommodation, transport, attractions and food. Hence, we can implement sustainable practices at different stages and in many activities.
1. Sustainable practices in transportation
I. Airlines
- Maintain a young fleet as far as possible as new technology helps to reduce carbon emissions.
- Also, choose non-stop flights.
- Airlines should encourage high load factor flights because when more people travel, the energy used per passenger decreases.
- And reduce operating weights as the less planes weigh, the less energy they use.
II. Cars
- Generally, promote the use of low-emission cars.
- Or replace old cars with environmentally friendly ones.
- And avoid SUVs as far as possible.
III. Railways and coaches
- Use renewable sources of energy.
- Recycle materials as much as possible.
- Likewise, renew infrastructure to attract more customers and decrease energy use.
- And improve customer service and trips to attract more tourists.
2. Accommodation
- Save energy with better air conditioning/heating systems.
- Generally, use energy-saving lighting systems such as sensors or even control vegetation growth.
- Opt for local foods to reduce transport costs.
- Likewise, invest in renewable energy sources like solar power.
- And recycle waste.
3. Tour operators
- Re-think and re-structure their distant destinations with closer ones.
- They should also develop low-carbon holidays such as train-based trips.
- And offer carbon offsets for flights.
4. Tourists
- Minimize air travel or choose alternative methods.
- Even travel less frequently and stay for longer periods of time.
- Likewise, voluntarily choose to offset flights that they cannot avoid.
- And choose airlines/destinations/services/activities that are eco-friendly.
Eco-tourism
Definition of ecotourism
According to The International Ecotourism Society,
‘ecotourism is the responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment. It also sustains the well-being of local people and involves interpretation and education.’
So, ecotourism is not only engaging in nature-based activities. Rather, it is a way to preserve the natural environment and sustain local communities.
History of ecotourism
Ecotourism first appeared in 1965 when Hetzer coined it with responsible travel. Eventually, other authors used it to refer to eco-development in parks in Latin America and Canada.
During the 1970s/80s’ environmental movement, the term became famous. Mass tourism was heavily degrading the environment and tourists wanted nature-based experiences.
At the same time, people in less developed countries were mutilating their natural resources for agriculture and development. They also realized that they could preserve their natural environment while gaining foreign currency.
Eventually, people used several different terms to promote concepts linked to ecotourism like responsible tourism. Some terms were vague in nature and we no longer use them. Others are basically subdivisions of ecotourism such as wildlife tourism.
Principles of ecotourism
For ecotourism to be successful, proponents must adhere to certain principles. These are:
- Keep environmental, behavioural, social and psychological impacts to a minimum.
- Likewise, respect the culture of host communities and their environment.
- Also, directly finance environmental conservation and host communities.
- Maximize tourist and host satisfaction.
- Build infrastructure that have the minimum impact on the environment.
- And, understand and recognize the spiritual beliefs of indigenous communities and help support them.
Ecotourism in Ecuador as an example
Perhaps one of the most successful ecotourism destination is Ecuador. Historically, it became a famous ecotourism site because of the rare species that inhabit the Galapagos Islands.
Eventually, though, many indigenous groups adopted ecotourism as part of their development strategy.
Today, a wide range of community groups including indigenous people, Afro-Ecuadoreans and mestizos work on diverse ecotourism projects. These range from the majestic Amazon forest to the high sierra and the coast of Ecuador.
Importance of ecotourism in Ecuador
Indeed, Ecuador is one of the most biologically diverse regions on Earth. The Oriente, especially, where the majority of the land belongs to indigenous communities like the Quicha, Achuar, Huaorani and Shuar is very rich.
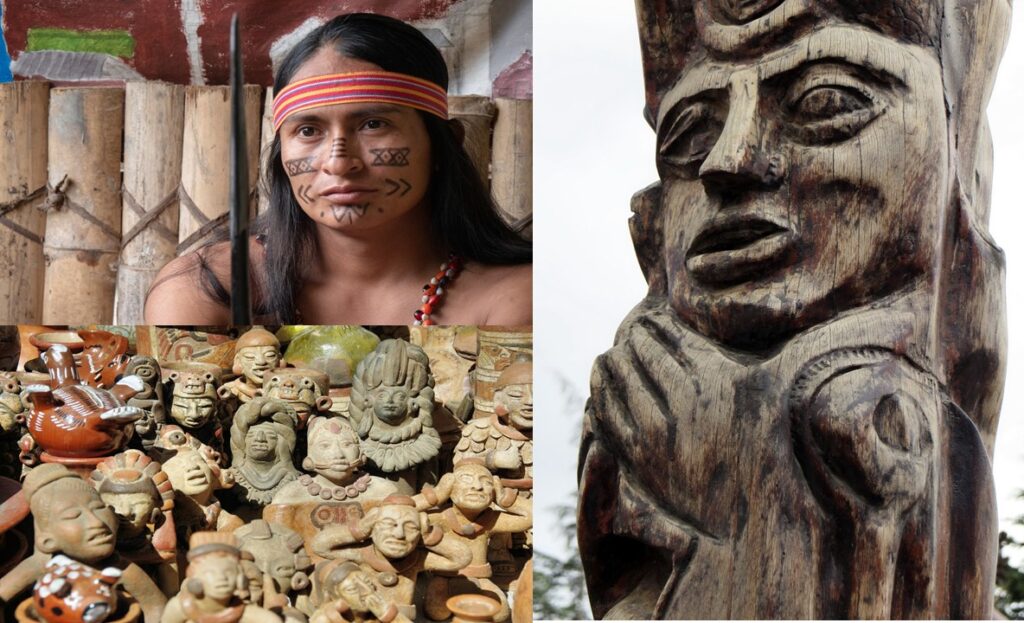

Ecotourism helped massively in the preservation of natural areas. Otherwise, investors would have destroyed the Amazon forest for oil.
In general, tour operators and NGOs help small communities to make the most of ecotourism based on their own terms. Thus, it allows indigenous people to sell traditional knowledge and use natural resources sustainably.
At the same time, it gives these communities much needed international support when they face tough decisions regarding the exploitation of natural resources. Additionally, it is a form of self-defence for indigenous communities. It helps them preserve their culture, traditional economies and remaining wild places on Earth.
For sure, small rural communities offer memorable experiences to tourists. They share their homes with them and teach them about their local customs and traditions. Or sometimes, they build eco-lodges in their localities with traditional materials and minimum impact on the environment.
Ecotourism activities
In general, ecotourism activities vary greatly from place to place. It typically revolves around the environment and the local customs of the community.
In Ecuador, the main ecotourism activities are
- Visiting the Ecuadorian forests (mangrove, cloud forest, high mountains etc.)
- Observing the flora and fauna
- Artisanal canoe rides and boat tours
- Forests, cliffs and beaches walks
- Artisanal fishing and octopus catching on rocky beaches
- Preparing and tasting traditional foods and drinks
- Artisanal fabric, jewelry, musical instruments, masks making
- Visits to sacred places, traditional shamans, midwives
Types of ecotourism
There are many subsectors that are related to ecotourism. We define them purely according to the principal attraction or product. They do not necessarily conform to the criteria applied specifically in ecotourism.
So, the main types of ecotourism are principally nature-based, wildlife, adventure, farm and cultural tourism.
Nature-based tourism
As a general rule, nature-based tourism refers to tourism where the natural features of the environment are the centre of attraction. It includes broad trips to visit landscapes or more specialized products like wildlife sightseeing. Camping, stargazing and birdwatching are examples of nature-based tourism.
Wildlife tourism
As for wildlife tourism, it is a large part of nature-based tourism itself. Wildlife tourism products vary greatly from terrestrial to marine tourism. The most common activities are safaris, guided rides, sport hunting, recreational fishing and animal feeding.
Adventure tourism
Adventure tourism refers to commercial tours where the principal attraction is an outdoor activity. This activity typically depends on the natural features of the terrain. It is exciting for the tourist and generally requires specialized sports equipment. Examples include skiing, snowboarding and surfing.
Farm tourism
Farm tourism in fact originates from bed-and-breakfast establishments and ranches. Today, many landholders are investing in it to provide tourists a unique experience of rural life and farming. Some examples are French vineyards, rice paddies in South-east Asia and dairy farms in the Swiss Alps.
Cultural tourism
In cultural tourism, tourists travel to experience different cultures and traditions. The aim is to learn and understand traditional cultures and visit historical sites. It includes folkloric music, art and dance, museums and traditional artefacts. An example is the traditional Kawa hot bath, in the Philippines.
Green tourism
History of green tourism
The term green tourism emerged in the 1980s referring to small groups of tourists visiting natural areas. They had the minimum impact on the environment. Eventually, people used it interchangeably with ecotourism and sustainable tourism.
Definition of green tourism
The UNWTO defines green tourism as
‘Activities that can we can maintain indefinitely in their environmental, social, economic and cultural contexts.’
Principles of green tourism
Basically, green tourism is a way to promote sustainable tourism.
As it is, the tourism industry will always have impacts given the large number of sectors involved. But, we can decrease these impacts.
Green tourism thus aims to help sectors engage in activities and make choices that have less environmental impacts, benefits society and the economy.
It includes ways to
- Reduce energy use,
- Also, minimize food miles,
- Promote biodiversity,
- And adopt sustainable practices.

Difference between sustainable tourism, ecotourism and green tourism
Finally,
- Sustainable tourism refers to the incorporation of sustainable practices in the tourism sector.
- Ecotourism is a branch of tourism.
- Green tourism is a catalyst to achieve sustainable tourism.
References
- Buckley, R., 2009. Ecotourism: Principles and practices. CABI.
- Maldonado-Erazo, C.P., del Río-Rama, M.D.L.C., Noboa-Viñan, P. and Álvarez-García, J., 2020. Community-Based Tourism in Ecuador: Community Ventures of the Provincial and Cantonal Networks. Sustainability, 12(15), p.6256.
- Weaver, D.B. ed., 2001. The encyclopedia of ecotourism. Cabi.

Pingback: Volcanic Eruptions: Positive and Negative Effects - Yo Nature
Pingback: Positive impacts of tourism on the environment - Yo Nature
Pingback: Negative impacts of tourism on the environment - Yo Nature
Pingback: The purpose of ecotourism with examples - Yo Nature